Contact us
Power of the Vagus Nerve: How VNS Therapy Offers Hope for Epilepsy and Depression
By Shaivana Bano
14 September 2025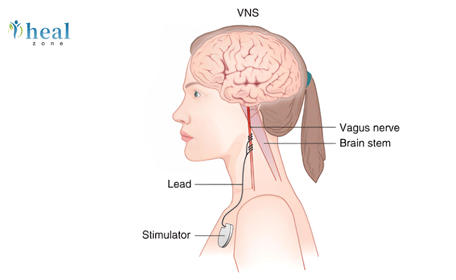
- What Is Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)?
- How Does VNS Work?
- Types of VNS Devices
- Who Is a Candidate for VNS Therapy?
- Benefits of VNS Therapy
- Risks and Side Effects
- VNS Procedure: Step-by-Step
- VNS Therapy Cost in India
- Top Hospitals for VNS in India
- Top Doctors for VNS Therapy in India
- Why International Patients Choose India for VNS
- VNS Beyond Epilepsy and Depression
- Conclusion: Is VNS Right for You?
- Quick Checklist Before Choosing VNS in India:
What Is Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)?
The vagus nerve is the 10th cranial nerve, extending from the brainstem to major organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive system. It serves as the body’s communication pathway, transmitting information between the brain and the rest of the body. VNS therapy involves using an implanted or external device to send controlled electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. These impulses help regulate abnormal brain activity, reduce seizures, and improve mood by influencing neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine.
This therapy is FDA-approved for the following conditions:
- Drug-resistant epilepsy (in children aged 4 years and older and adults)
- Treatment-resistant depression (in adults who have not responded to multiple antidepressants)
How Does VNS Work?
When the vagus nerve is stimulated, signals travel to key areas of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, and limbic system. This stimulation helps to:
- Reduce hyperexcitability in epilepsy patients
- Enhance mood-regulating circuits in individuals with depression
- Improve brain plasticity and recovery
While the exact mechanisms are still being researched, long-term clinical trials indicate that VNS can reduce the frequency of seizures by 50% or more in many patients and help individuals with severe depression experience meaningful improvements after several months of therapy.
Types of VNS Devices
There are different types of VNS systems available today:
Implantable VNS Devices
These devices are surgically placed under the skin in the chest and connected to the left vagus nerve in the neck. The main models include:
- VNS Therapy® (LivaNova) – the most widely used system globally.
- AspireSR® – automatically detects seizure-related changes in heart rate and delivers stimulation.
- SenTiva® – a next-generation model with advanced programming, day/night cycles, and responsive features.
Non-Invasive VNS Devices (tVNS / nVNS)
These devices do not require surgery and stimulate the vagus nerve externally:
- GammaCore® (electroCore) – a handheld device applied to the neck, FDA-cleared for treating migraines and cluster headaches.
- Auricular tVNS devices – stimulate the vagus nerve branches in the ear and are used in research for epilepsy and mood disorders.
Emerging Devices
- Closed-loop VNS systems are being developed that will detect seizure activity in real-time and deliver targeted stimulation.
Who Is a Candidate for VNS Therapy?
For Epilepsy Patients:
- Individuals who have failed at least two anti-seizure medications
- Patients with drug-resistant epilepsy who are not suitable candidates for brain surgery
- Children aged 4 years and older with uncontrolled seizures
For Depression Patients:
- Adults with major depressive disorder who have not improved with four or more medications
- Patients with chronic or recurrent depression
Not Suitable For:
- Individuals with severe heart rhythm issues
- Patients who are unfit for anaesthesia
- Those who have undergone bilateral vagotomy
Benefits of VNS Therapy
- Seizure Control: Many patients experience a 50–70% reduction in seizure frequency.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients often see fewer hospitalisations, reduced seizure severity, and improved mood.
- Adjunctive Therapy: VNS can be used in conjunction with medications, potentially allowing for dosage reductions.
- Long-Term Effectiveness: The benefits of VNS often increase over time, unlike some drug therapies.
- Mood Stabilisation: VNS has a positive impact on mood and alertness, even in patients with epilepsy.
Risks and Side Effects
While VNS is generally safe, patients may experience:
- Hoarseness or voice changes
- Throat discomfort during stimulation
- Mild coughing or shortness of breath
- Surgical risks, such as infection or bleeding
- Rarely, a device malfunction or issues with the leads
- Most side effects tend to diminish after adjustments to device programming.
VNS Procedure: Step-by-Step
1. Pre-Surgery Evaluation: A neurologist or psychiatrist evaluates and confirms candidacy.
2. Implant Surgery: A small generator is placed under the skin in the chest area, and a wire is connected to the vagus nerve in the neck. Duration: 1–2 hours.
3. Programming: The device is activated 2–4 weeks post-surgery and is customised by the doctor.
4. Follow-Up: Regular outpatient visits are required to adjust settings for maximum benefit.
5. Battery Replacement: Depending on the device model, replacement is needed every 5–10 years.
VNS Therapy Cost in India
One major reason patients travel to India for VNS is its affordability.
Average Cost: USD 20,000 – 30,000 (includes device, hospital stay, surgeon, and follow-up)
Factors Affecting Cost:
- Type of device (SenTiva, AspireSR, Standard VNS)
- Choice of hospital (public vs. private)
- Additional investigations (MRI, long-term EEG)
Always request an itemised quotation that includes:
- Device cost
- Surgery charges
- Hospital stay
- Post-operative programming
Top Hospitals for VNS in India
India hosts several world-class epilepsy and neurosurgery centres:
- Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram: Renowned for epilepsy surgery.
- Apollo Hospitals, Chennai & Hyderabad: Leading private chain with comprehensive epilepsy care.
- Fortis Hospitals (Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore): Advanced facilities for neurosurgery.
- Max Super Speciality Hospital: Strong programs in neurology and epilepsy.
Top Doctors for VNS Therapy in India
Several neurosurgeons and epileptologists perform VNS implants; notable names include:
- Dr. V. P. Singh at Medanta, Gurugram (specialist in epilepsy surgery and neuromodulation)
- Dr Sandeep Vaishya / Dr Rana Patir at Fortis Memorial Research Institute
Here is a list of the leading neurosurgeons who specialise in performing this surgery.
Tip: Always choose a doctor involved in a dedicated epilepsy surgery program rather than a general neurosurgeon.
Why International Patients Choose India for VNS
- Affordable Cost: Treatment in India can be 60–80% cheaper than in the USA or Europe.
- Experienced Doctors: India has some of the most skilled neurosurgeons in Asia.
- Modern Hospitals: NABH & JCI-accredited hospitals with cutting-edge technology.
- Short Waiting Times: Quick scheduling available for international patients.
- English-Speaking Staff: Facilitates easy communication and patient-friendly services.
- Medical Tourism Support: Assistance available for visas, accommodation, translators, and follow-up.
VNS Beyond Epilepsy and Depression
Research continues into VNS applications for:
- Migraines & cluster headaches (using non-invasive devices)
- Stroke rehabilitation
- Chronic pain syndromes
- Inflammatory conditions
While promising, these uses remain experimental and are not considered standard treatment.
Conclusion: Is VNS Right for You?
Vagus Nerve Stimulation therapy has transformed the lives of thousands of patients with epilepsy and depression worldwide. In India, treatment is available at world-class hospitals at a fraction of the cost found globally.
If you struggle with uncontrolled seizures or treatment-resistant depression, VNS may be worth discussing with a specialist.
Quick Checklist Before Choosing VNS in India:
- Confirm your candidacy through a comprehensive evaluation.
- Select a hospital with a dedicated epilepsy program.
- Obtain an itemised cost estimate (including device type).
- Plan for long-term follow-up visits to adjust the device as needed.
With the right doctor and hospital, VNS therapy in India can lead to a safer, healthier, and more independent life.
Contact us
Written by
B.Sc. & M.Sc. in Medical Imaging Technology
Frequently Asked Questions
No, it reduces seizure frequency and severity but is not a cure.
Yes, though doses may be lowered if seizures improve.
Yes, devices like gammaCore provide non-invasive stimulation, but implantable VNS is more established for epilepsy.


Dr. Sandeep Vaishya
MBBS, MS, MCh, Fellowship
Neurosurgeon, Spine Surgeon
36 Years Years of Experience

Latest Blogs
Reviews
I am Fadel Abu Muhammad from Tal Afar, Iraq My father had a brain tumor. We traveled to India to Accord Specialty Hospital, New Delhi, through a resident professor, Muhammad, Dr. Vikram, who called for a laparoscopic tumor removal operation. Thank God I thank the translator, the doctor, and all the hospital staff.
Posted On
I am Muhammad Reda from Baghdad, Iraq I was suffering from weakness in my left hand. I underwent tests and it turned out that I had a brain tumor. The translator, Muqeem Muhammad, contacted us and we traveled to India. I had a neuronavigation procedure performed by Dr. Sandeep Vashya Praise be to God, the operation was completed successfully on the computer At Fortis Hospital New Delhi I thank the translator and the doctor
Posted On
All our gratitude and appreciation to the wonderful translator Mohammed Muqeem, who was truly a great support and companion during our journey for my mother’s treatment in India. He was extremely helpful, deeply understanding of all our needs, patient, and dedicated in his work, which eased a lot of the hardship and challenges we faced being away from home. His presence with us was not just about translating words but about offering real human support in every situation and every moment. May God bless him and reward him greatly for all he has done for us.
Posted On
I'm Emad Mohammed Khadir from Iraq. I was suffering from cirrhosis and liver cancer. I came to Fortis Hospital in India to see Dr. Ankur Bahil, a consultant oncologist, with the help of our translator, resident professor Mohammed Al Hindi. Thank God, we received our chemotherapy doses. The doctor and all the hospital staff were very kind and helpful. May God bless them all. Thank you.
Posted On
I am Redha Fadel from Nasiriyah, Iraq. I had a bone tumor, osteosarcoma. I traveled to India to see Dr. Ankur, a cancer specialist at Fortis Hospital, with the help of Hill Zone Medical Tourism Company, Professor Muqeem Muhammad Al Hindi. I thank you for your humanity and services.
Posted On
Peace be upon you. I am from Iraq. My brother is suffering from a tumor in his left thigh (osteosarcoma). We came to Al-Nahda for treatment. We stayed at Fortis Hospital for two months. We are now going to Iraq and will return to India to complete the treatment and the joint replacement surgery. I would like to thank the polite Indian translator, Muqeem Mohammed Al-Hindi. He was our brother before he was a translator and he helped us a lot with my brother's illness. Thank you, Muqeem. Thank you, Fortis Hospital. Thank you, Dr. Ankur.
Posted On
Peace be upon you, I'm from Iraq. My name is Majid Mazhar Kazim. My brother was suffering from tumors, so we contacted a resident professor, Muhammad Al-Hindi, and we sent him medical reports. He received us from the airport in New Delhi. I highly recommend him to Iraqi patients. He is helpful and well-mannered. He didn't hold back on us and didn't leave us alone from the first day until the last. He also took us to the airport. I thank them all.
Posted On
I am Mohammed Kazim from Iraq, from Babylon. My brother Mushtaq was suffering from meningitis. We came to India to Fortis Hospital through our resident professor, Mohammed, the director of Hill Zone Medical Services. I thank them for their kind treatment and translation. It was an enjoyable and fruitful trip. Praise be to God.
Posted On
I am from iraq tilafar, i came to India for my treatment an immune disease, i am thankful to Mr Muqeem and hospital staff, Marego Asia Hospital
Posted On
I am from Iraq. My son was suffering from Hirayama disease. I called Heal Zone, and they arranged our treatment journey. Now my son is in good health, and his finger movement has come back.
Posted On